Anxiety Vs Panic Attack: Understanding The Difference
Published on 14th June, 2024

With mental health issues on the rise, anxiety and panic attacks are often misunderstood or used interchangeably. Despite their similarities, these conditions differ significantly in their triggers, symptoms, and management. A clear understanding of the differences between anxiety and panic attacks is essential for effective treatment and support.
Anxiety: A chronic condition
Anxiety is a normal reaction to stress and can even be beneficial in certain situations. However, it becomes a concern when it persists and impacts daily functioning. Anxiety is characterised by persistent and excessive worry about various aspects of life, such as work, health, or relationships (Cuncic, 2023).
Symptoms of anxiety
Anxiety manifests both psychologically and physically. Common symptoms include:
● Constant worry or fear
● Restlessness or feeling on edge
● Fatigue
● Difficulty concentrating
● Irritability
● Muscle tension
● Sleep disturbances
Physically, anxiety can cause symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, shortness of breath, and gastrointestinal issues. These symptoms tend to be chronic and can fluctuate in intensity.
Triggers of anxiety
Anxiety triggers are diverse and multifaceted, often stemming from life stressors, genetic predisposition, or environmental factors. Specific situations like job interviews, financial concerns, or social interactions can heighten anxiety levels.
Management of anxiety
For mild to moderate cases, managing anxiety typically involves a combination of therapy and lifestyle changes. Cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) is one of the most effective treatments, helping individuals identify and challenge irrational thoughts. This approach is also crucial for identifying anxiety in children, as early intervention can significantly improve outcomes. For more severe cases of anxiety, medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) may also be prescribed. Additionally, mindfulness practices, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can significantly reduce anxiety symptoms (Curtiss et al., 2021).
Panic attacks: sudden and intense
Panic attacks are sudden episodes of intense fear or discomfort, often occurring without a clear trigger. These episodes peak within minutes and are accompanied by severe physical and psychological symptoms (Ankrom, 2024).
Symptoms of panic attacks
The symptoms of a panic attack are intense and can be frightening, often mimicking those of a heart attack. They include:
● Rapid heart rate
● Sweating
● Trembling or shaking
● Shortness of breath or a feeling of being smothered
● Chest pain or discomfort
● Nausea or abdominal distress
● Dizziness or light-headedness
● Chills or hot flashes
● Numbness or tingling sensations
● Feelings of unreality or detachment
● Fear of losing control or going crazy
● Fear of dying
These symptoms are typically short-lived, lasting around 20 minutes, but the fear of another attack can lead to ongoing anxiety and avoidance behaviours.
Triggers of panic attacks
While some panic attacks occur without a clear trigger, others may be precipitated by specific situations or stressors. Common triggers include:
● Major life transitions or stressors (e.g., loss of a loved one, job loss)
● Phobias
● Chronic illness
● Substance abuse
● Certain medications
Management of panic attacks
Effective management of panic attacks often involves both immediate and long-term strategies. In the moment, deep breathing exercises and grounding techniques can help manage the acute symptoms. Long-term management includes therapy, such as CBT, which can help individuals understand and change their thought patterns. Medications, particularly anti-anxiety drugs or antidepressants, may also be used to reduce the frequency and severity of panic attacks.
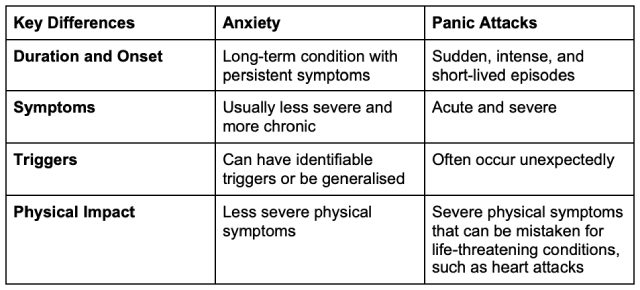
Key differences between anxiety and panic attacks
While anxiety and panic attacks share some similarities, their differences are significant:
Conclusion
Recognising the difference between anxiety and panic attacks is important. If you experience these symptoms, seeking help from a mental health professional can ensure you get the right diagnosis and treatment. Both conditions are manageable with the right approach, combining therapy and lifestyle changes.
In Singapore, there are resources available for all ages. A child's therapist in Singapore can provide specialised support for young individuals dealing with anxiety, while adult counselling in Singapore offers tailored interventions for managing anxiety and panic attacks in adults. Accessing these resources can lead to improved mental health and a better quality of life.
Understanding the unique characteristics of anxiety and panic attacks empowers individuals to take the first step toward effective management and recovery, leading to a healthier and more balanced life.
References
Ankrom, S. (2024, January 16). Panic Attack vs. Anxiety Attack: How They Differ. Verywell Mind. https://www.verywellmind.com/anxiety-attacks-versus-panic-attacks-2584396
Cuncic, A. (2021). The Characteristics of High-Functioning Anxiety. Verywell Mind. https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-high-functioning-anxiety-4140198
Curtiss, J. E., Levine, D. S., Ander, I., & Baker, A. W. (2021). Cognitive-Behavioral Treatments for Anxiety and Stress-Related Disorders. Focus (American Psychiatric Publishing), 19(2), 184–189. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.focus.20200045